What Is a Birthmark?
Birthmarks are blemishes on the skin that are noticeable at birth, or shortly afterwards. Birthmarks may be caused by extra pigment in the skin or by blood vessels that do not grow normally. According to folklore in Spain, Italy and some Arabic countries, birthmarks were caused by the unsatisfied wishes of the mother during pregnancy. For example, if a craving for strawberries was not satisfied, her child would be born with a strawberry mark on his/her skin. All birthmarks should be checked by a doctor.
Salmon Patches
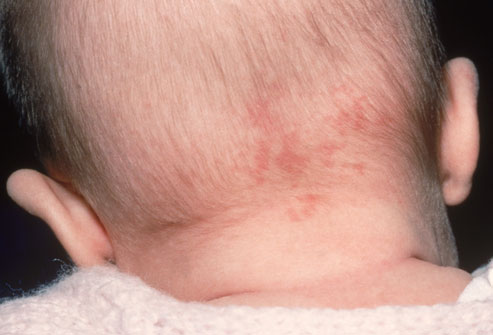

Salmon patches are nests of blood vessels that appear as small, pink, flat marks on the skin. They occur in 1/3 of newborn babies. Salmon patches can appear on the back of the neck (“stork bite”), between the eyes (“angel’s kiss”), or on the forehead, nose, upper lip, or eyelids. Some fade as baby grows, but patches on the back of the neck usually don’t go away. Salmon patches require no treatment.
Port Wine Stains
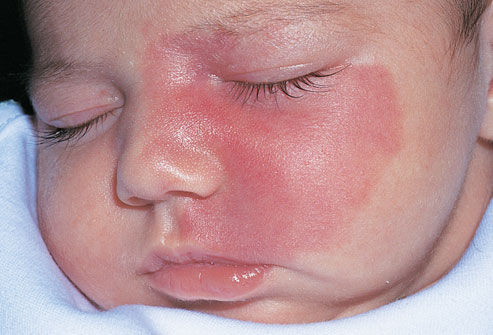
A port-wine stain is a type of birthmark that is caused by a malformation of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. The name port-wine stain comes from the color of the birthmark, which ranges from light pink to a dark red color. The difference between these birthmarks is that salmon patches tend to fade in the first year of life while port-wine stains become darker and grow along with the baby. Those on the eyelid may increase the risk of glaucoma. Port wine stains may be a sign of other disorders, but usually not. Treatment includes laser therapy, skin grafts, and masking makeup.
Mongolian Spots
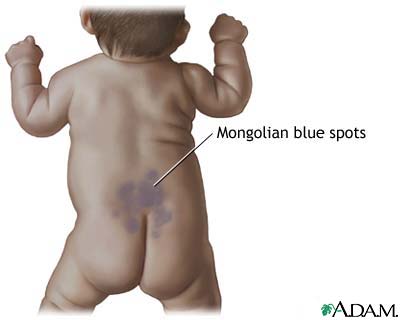
Mongolian spots are blue to slate gray in color, these marks resemble bruises, but are in no way sensitive to the touch. They may show up on your baby's back, buttocks, or legs and vary from really tiny (like a pinhead) to pretty big (six inches or more across).Mongolian spots are most common on darker-skinned babies. They usually fade by school age, but may never disappear entirely. No treatment is required.
Cafe-Au-Lait Spots
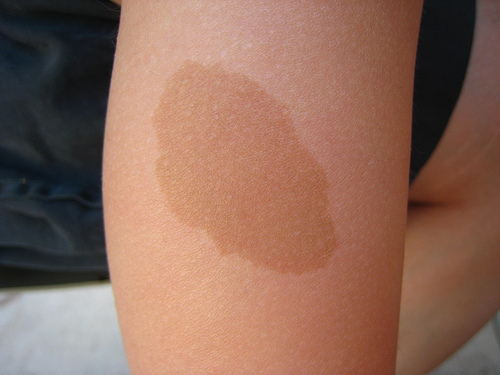
A café au lait macule (CALM) is a well-defined, flat area that is darker in color than the rest of the skin. The term refers to the characteristic even (homogeneous) color of "coffee with milk," which may be light to dark brown. Café au lait macules usually appear first in early childhood, although they may be present at birth. They may be single or multiple, and they increase in size as the person gets older. Café au lait macules can be indicators of more extensive (multisystem) disease, particularly neurofibromatosis.
Strawberry Hemangiomas
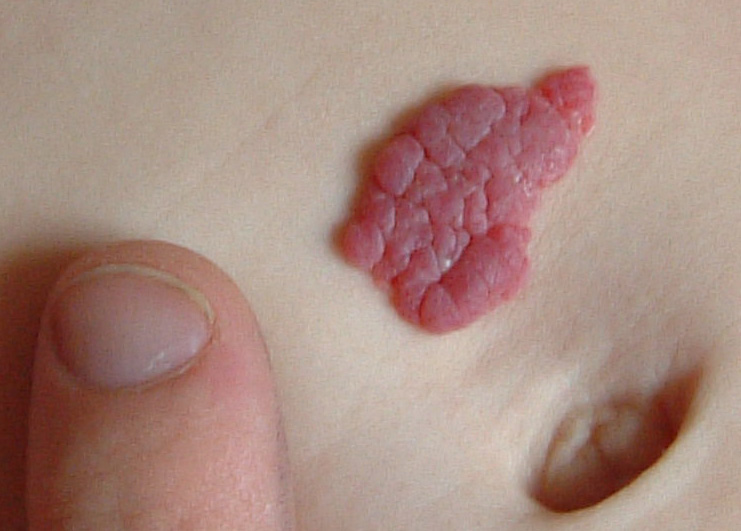
Hemangiomas are a collection of small, closely packed blood vessels. Strawberry hemangiomas occur on the surface of the skin, usually on the face, scalp, back, or chest. They may be red or purple; they can be flat or slightly raised, with sharp borders.
Strawberry hemangiomas usually develop a few weeks after birth. They grow rapidly through the first year before subsiding around age 9. Some slight discoloration or puckering of the skin may remain at the site. No treatment is required, but when desired, medicines and laser therapy are effective.
Cavernous Hemangiomas
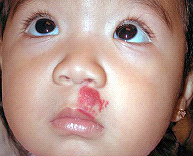
Present at birth, deeper cavernous hemangiomas are just under the skin and appear as a bluish spongy mass of tissue filled with blood. If they’re deep enough, the overlying skin may look normal. Cavernous hemangiomas typically appear on the head or neck. Most disappear by puberty.
Venous Malformation
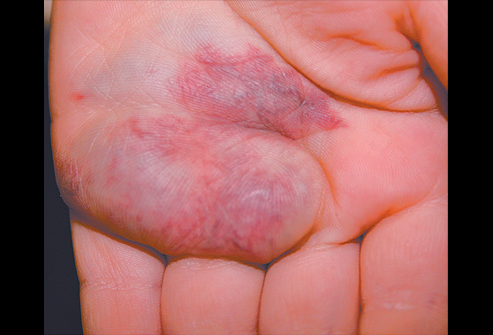
A VM is a bluish lesion that’s the result of improperly formed veins. The walls of these veins are unusually thin because of a relative lack of smooth muscle cells — and that’s why they can stretch and cause problems. VMs can appear anytime during childhood, adolescence or adulthood. Most are present at birth, though they may not be diagnosed until later— especially if your child’s lesion is small or not in an obvious location. They’re most common in the skin, but can be present in other tissues and organs as well. Treatment -- often sclerotherapy or surgery -- may be necessary for pain or impaired function.
Pigmented Nevi (Moles)
Moles occur when cells in the skin grow in a cluster instead of being spread throughout the skin. They can appear anywhere on the body, alone or in groups. Moles are usually flesh-colored, brown, or black. Moles may darken with sun exposure and during pregnancy. They tend to lose color during adulthood and may disappear in old age. Most moles are not cause for alarm. However, moles may have a slightly increased risk of becoming skin cancer. Moles should be checked by a doctor if:
• They change size or shape.
• They look different from other moles.
• They appear after age 20.
Congenital Nevi

Congenital nevi are moles that appear at birth. The skin texture may range from normal to raised, or nodular to irregular. Congenital nevi can grow anywhere on the body and vary in size --from a small 1-inch mark to a giant birthmark covering half of the body or more. Small congenital nevi occur in 1% of newborns. Most moles are not dangerous. But congenital nevi, especially large ones, should always be evaluated by a doctor since they may have an increased risk of becoming skin cancer.
Dysplastic Nevi (Atypical Moles)
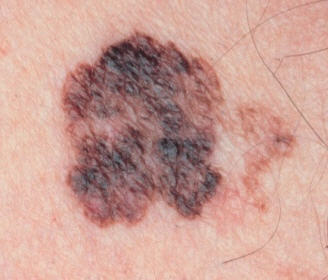
Atypical moles are generally larger than ordinary moles and have irregular and indistinct borders. They may resemble cancerous moles. They may have a mix of colors including pink, red, tan and brown. These moles tend to be hereditary. Atypical moles have an increased chance of developing into melanoma skin cancer. Have a doctor evaluate all moles that look unusual, grow larger, or change in any way.
Your Baby checkup
what are the vaccinations that he should have taken until now?
Generate a report for my baby.
Track Your Baby Vaccinations
Find Your Baby name
Mohandessin
01002195777
01000012400
0233048350
Beverly Hills
01000012900
0238576831
El Tagamo3
Al Sheikh Zayed
02- 38514031
01000608597


